 |
| https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/originals/d3/d5/51/d3d5510cbfa3937aaabf622cd0504617.jpg |
 |
| https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/736x/df/c8/ea/dfc8ea2efb99aafce89c9c8ee4f4dcfb.jpg |
It involves the structure of bones, the muscle and cartilage which is underneath our skin on the face. When we do make-up for the models or actors, it is important to know where the bones structure and so for example we will know where to do the highlight and contouring, etc. In special effects make-up, it is also concern the face and even body structure of the human body as sometimes you will want to remodeling a face to create your design of a character.
The bones on the face:
The skull is used to protects our brain, the eyes and also helps to delicate the structures of the ears. It forms the shape of the face and the head and also attached to the teeth and muscles as well. 'The bones are joined by sutures (immovable joints) with the exception of the mandible (lower jaw-bone), which is hinged and therefore moveable.' (Conway, 2004)
 |
| http://idey.me/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/face-shape.jpg |
When we know the names of the bones, we can point out exactly what area on the face we want to discuss on. For the forehead, 'there are two separate and distinct eminences, the frontal and the superciliary, which must ordinarily be considered separately in highlighting.
When source of light is directly overhead, forming a slight shadow between the two.' When we try to age a character, it is very important to know the changes on the bones structure, the muscles and the cartilage due to the age of the character. The only movable part on the skull is the mandible
Body:
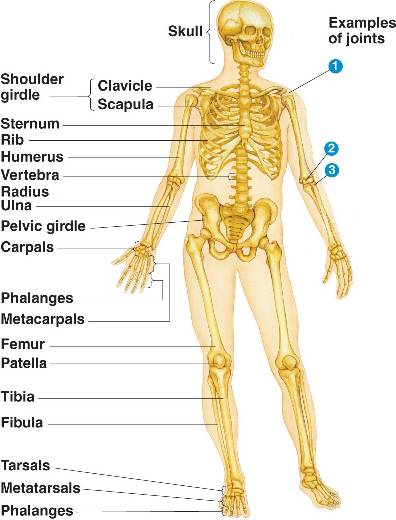 |
| http://bio1152.nicerweb.com/Locked/media/ch50/50_34aHumanSkeleton-L.jpg |
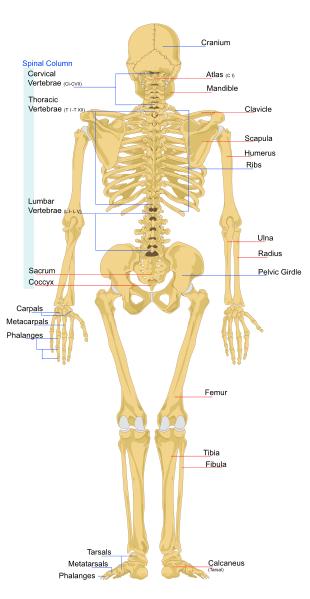 |
| http://www.ducksters.com/science/bones_back.jpg |
Age:
 |
| http://drballe.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/aging-06-big.jpg |
When a person beyond middle life, their skull structure will usually change and becomes more protruding. You can see more clearly if the person is thin. If the person is large and abundant, the skin will become flabbiness and double chins and pouches will be seen clearly. When people getting older, the skin will become more saggy. Hair may fall out and the eyebrows may become scraggly or bushy. The tip of the nose and the skin on the neck may droop as well. The teeth may fall out and the lips will become thinner than before. The hair color and also the skin will change. Wrinkles will be seen on the face, neck and hands and the hands may become bony. The nasolabial folds are creases which located from the nose to the lips and it will be seen more clearly when a person gets older.
Nose-
The upper section of the nose is named of the nasal bone, but on the lower part of the nose, it is considered as cartilage which attached to the nasal bone.
Cheekbones-
The cheekbone, also known as the zygomatic arch is very important as when you do the contouring or apply blusher on the face, you need to see where it is located. Some people have protruding cheekbones and some people may need to feel them with their fingers. You can start by touching the top of the bone and then feel how it curves from the bottom of the cheekbones until you feel the bone under the eye. The angle of the cheekbones slope down from the ear and toward the center of the face.
Hollows-
There are the hollows in the skull and they are the orbital hollows, also known as the eye sockets and the temporal hollows which we usually referred to 'the temples'. The temporal hollows are not very deep, but due to the increasingly with age, it will be seen more clearly. The infra-temporal hollows are located under the cheekbones area. The lack of bony support makes the flesh to sink in underneath the cheekbone.When designing for old people or starvation character, the infra-temporal hollows will be sink in clearly.
Muscles on the face:
There are three types of muscles tissue and they all help to cause movements and they are:
- voluntary muscle tissue ( it is attached to the bone)
- involuntary muscle tissue ( it is found inside the digestive and urinary tract and also the walls of the blood vessels)
- cardiac muscle tissue (it is found in the walls of the heart)
 |
| http://hair-and-makeup-artist.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/Facial-Muscles.jpg |
- Frontalis- It is located at the upper part of the cranium. It helps to raise our eyebrows.
- Corrugator- It is located at the inner corners of the eyebrows. It helps us to frown.
- Procerus- It is located at the top of the nose between the eyebrows. It is used to form wrinkles over the bridge of the nose and depresses the eyebrows.
- Orbicularis Oculi- It is surround the eye area. It helps us to close our eyes and blink.
- Nasalis- It is located over the front of the nose. It is used to compresses the nose which causes wrinkles
- Temporalis- It is located from the side of the face and runs towards the upper jaw. It helps us to chew food and close our mouth
- Masseter- It runs down and back to the angle of the jaw and is used to lift the jaw and gives the teeth strength when biting something.
- Buccinator- It is used to puff out the cheeks when we keep food in our mouth when chewing, blowing, etc. It forms most of the cheek area and provide shape.
- Risorius- It is located in the lower cheek and joins to the corner of the mouth. It helps to pull back angles of the mouth for instance, when we smile.
- Zygomaticus- It runs down the cheek towards the corner of the mouth. It helps to pull the corner of the mouth upwards and sideways.
- Quadratus labii superiorus- It runs upward from the upper lip and it helps to lift the upper lip and open the mouth.
- Orbicularis oris- It surrounds the lips and is used to form the mouth. It helps us to close our mouth and pushes the lips forward.
- Mentalis- It forms the chin and helps to lift the chin and also moves the lower lips outwards.
- Traiangularis- It is located from the corner of the lower lip to over the chin. It hepls to pull the corner of the chin down.
 |
| http://humandiagram.info/wp-content/uploads/Muscles-of-the-Human-Body.jpg |
- Mentalis - it is used to lift the chin and moves the lower lips outwards
- Triangularis- it is from the corner of the lower lip and extends over the chin. It helps to pull the corner of the chin down
- Trapezius- it is from the sides of the neck to the upper back. It helps to rotate the shoulders, pull our head back, rotation of our head and draws back the scapula bones.
- Pectoralis- It is located at the front of the chest and under the breasts. It helps to pull our arms forwards and rotation of the arms.
- Deltoid- It is used to raise our arm from the side and pulls it backwards and forwards. It is located on the caps the shoulder.
- Occipitalis- It is located at the back of the skull and is used to help with the movement of the head.
The skin:
The skin is used to cover the body and it varies in thickness on different parts of the body. The thinnest skin is on the lips while the thickest is on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands as it is used to protect against friction,. Because the skin covers up the entire body, it can suffer from skin diseases or disorders.
The functions of the skin-
- Vitamins - Ultra- violent light hits the skin and turns into the synthesis of vitamin D
- Sensory - the skin sensory nerve endings allow us to feel pain, temperature, pressure and touch
- Heat regulation (homeostasis)- the skin helps to regulating body's temperature such as when we are warm, we do sweat while we are cold, the hairs in the skin stand on end to trap warm air
- Absorption - the skin helps for absorbing small amounts of products when we apply on the surface of the skin
- Protection- Melanocytes protect the body against UV damage by producing melanin. The acid Mantle protects against the invasion if microbes and dehydration. The cushioned layer of the subcutaneous layer of the skin protects the underlying structures against minor trauma
- Excretion- Waste products and toxins, for instance, urea, are remove by the skin from the body in the form of sweat.
- Secretion- The skin produce and discharge sebum onto its surface.
The structure of the skin-
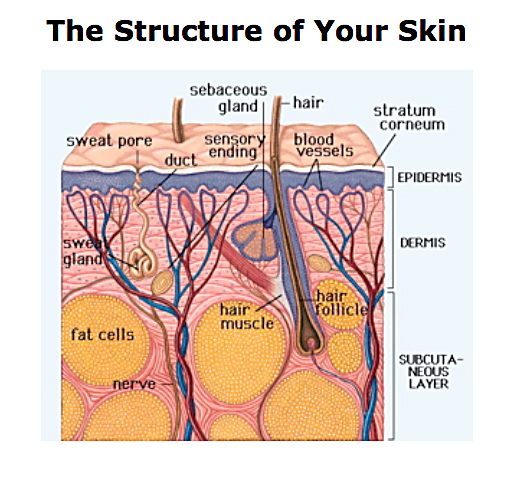 |
| http://7cream.ca/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/skin.jpg |
The Epidermis:
It is made up by five layers of cells. The lower two layers have got living cells while the three outer layers have got cells which have died as a results of the process of keratinisation. There is no blood or nerve in the epidermis, but in the deeper layers, it is bathed in interstitial fluid from the dermis which allows the nutrients and oxygen to carry the cells to these layers.
The five layers are:
- Stratum germativum or basal/ germinating layer - deepest layer
- Stratum spinosum or prickle cell layer
- Stratum granulosum or granular layer
- Stratum lucidium or clear layer
- Stratum corneum or horny layer- outermost layer
The Dermis:
It lie below the Epidermis and is composed of collagen fibres which helps to provide strength and support. It also contains elastin fibres which provide elasticity. The Dermis has two layers and they are superficial papillary layer and the deep reticular layer.
- The Superficial papillary layer is composed of adipose connective tissue and it is connected to the underside of the epidermis using projections named dermal papillae. It is used to aid nutrition of the epidermal cells for increasing the surface area where oxygen and nutrients can pass from the dermis. The dermal papillae has got nerve endings, network of blood and also lymphatic capillaries.
- The Deep reticular layer is the layer under the papillary layer and it is formed of tough fibrous connective tissue.
The Subcutaneous layer:
It is thick , an insulating layer of fat and connective tissue which is below the dermis. It helps to support fragile structures for example, the lymph and the blood vessels. It consists of adipose tissue which takes the role of the formation and storage of fat. This layer helps to keep the body warm and protect the body.
Veins
Veins
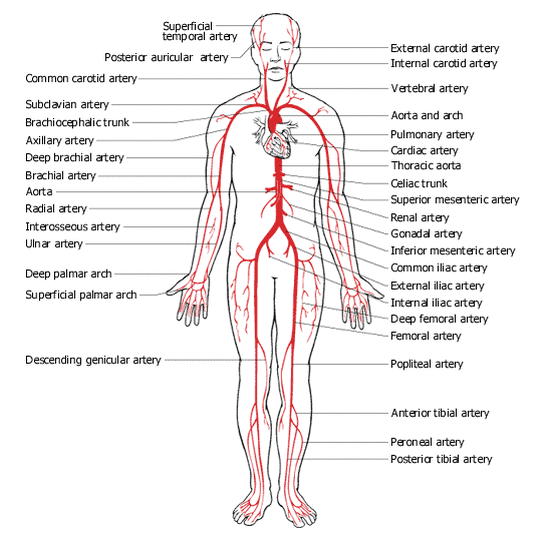 |
| http://kirstenwrightanatomy.weebly.com/uploads/1/3/9/5/13959705/2430093.gif?552 Arteries |
 |
| http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/isr/anatomy/anatomy2/venous.gif Veins |
 |
| https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/736x/0e/17/41/0e1741b24fa29658587c0ed09b5282b2.jpg Blue color: Veins Red color: Arteries |
By know which directions the veins go, it is important for special effects make-up as if you are creating something like scars, cuts, bruises, etc, you will need to think of how the veins appear on the skin, what color it has become, etc.
References:
- Corson R., Norcross B., Glavan J.(2010). Stage Makeup. Tenth edition. Publisher: Allyn & Bacon.
- Conway J. (2004). Make-up artistry for professional qualifications. Published by Heinemann Educational Publishers.
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/21c/keeping_healthy/heartdiseaserev2.shtml
No comments:
Post a Comment